Understanding Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
(Pediatrics Center) article author : Pucharawan Chuenrattanawong, M.D.

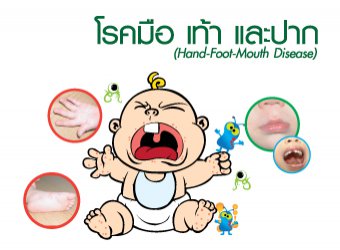
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
is a common viral infection in young children, caused by the Enterovirus group, such as Coxsackievirus. This disease mostly affects children under the age of 5, especially during the rainy season.
Transmission
HFMD spreads through contact with bodily fluids such as saliva, mucus, or feces of an infected person, or by touching objects contaminated with the virus.
Symptoms
1. High fever
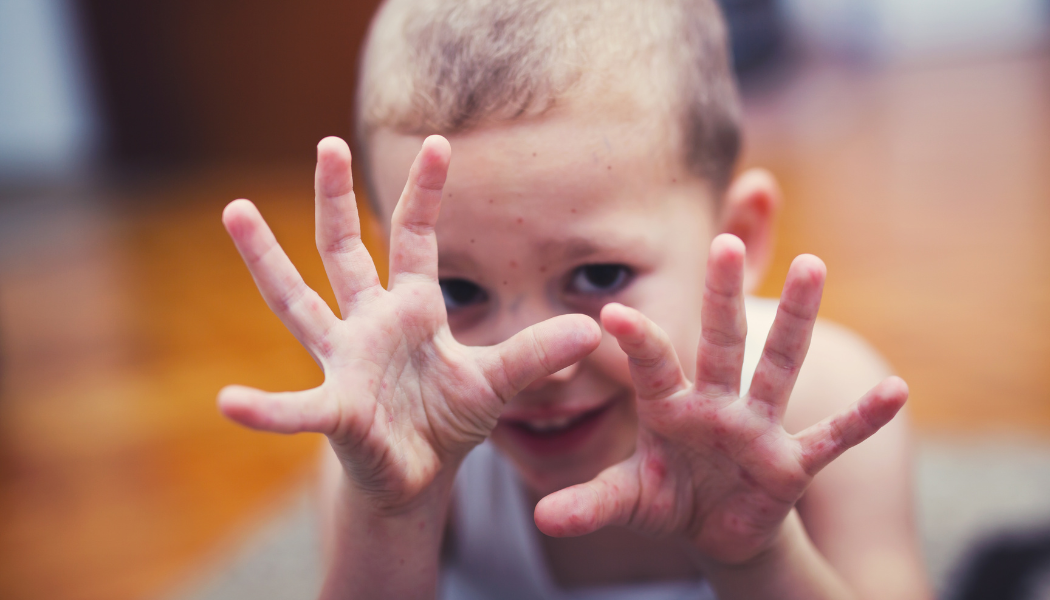
2. Rash or blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth
3. Sores in the mouth, causing pain and reluctance to eat or drink
4. Diarrhea or vomiting in some cases
Treatment
HFMD usually resolves on its own within 7-10 days. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as reducing fever and keeping the child hydrated. In some severe cases, medical attention may be required.