Awareness is Prevention! Cervical Cancer Warning Signs and Symptoms at Each Stage
(Obstetrics & Gynecology Center) article author : Admin

Awareness is Prevention! Cervical Cancer Warning Signs and Symptoms at Each Stage
Did you know that aside from breast cancer, which is the leading health threat to women, cervical cancer is another critical concern, ranking as the second most common cancer among women?
This article invites women everywhere to recognise the warning signs, understand the five key risk symptoms of cervical cancer, and adopt preventive measures to stay safe from this disease.
Understanding Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer occurs in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It is primarily caused by persistent infection with the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), typically contracted through sexual contact. The body’s immune system often fails to eliminate the virus, allowing it to persist and eventually cause cellular abnormalities that may lead to cancer.
Who Is at Risk of Developing Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer is most commonly found in women aged 35–60 and can affect any woman who has been sexually active. Key risk factors include:
- People who engage in sexual activity at a young age
- Multiple sexual partners
- Sexual partners with multiple other partners
- A weakened immune system or behaviours that compromise immunity, such as regular smoking
- A history of other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Warning Signs of Cervical Cancer Every Woman Should Know
Although cervical cancer is common, it can be treated effectively if detected early. Look out for the following symptoms to seek timely medical care:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding: This may include bleeding after intercourse, spotting between periods, heavy or prolonged menstrual flow, or postmenopausal bleeding.
- Unusual vaginal discharge: This may appear yellow or brown, sometimes mixed with blood, and may have an unpleasant odour or resemble watery, mucous, or pus-like secretions.
- Loss of appetite and fatigue: Often accompanied by unexplained weight loss.
- Pelvic pain: Persistent pain in the lower abdomen unrelated to menstruation.
- Pain during intercourse: Caused by pressure or constriction in the vaginal area.
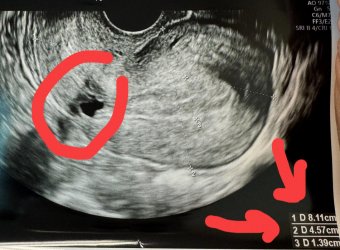
Symptoms by Stage of Cervical Cancer
If you notice potential warning signs, further investigation is necessary to determine the stage of cervical cancer, classified as follows:
Stage 1: Cancerous cells are confined to the cervix. Symptoms may be mild or absent but can include light post-coital bleeding or abnormal vaginal discharge.
Stage 2: Cancer begins to spread to the upper vagina or surrounding cervical tissues. Symptoms such as irregular discharge, spotting, and pelvic pain may become more noticeable.
Stage 3: Cancer extends to the lower third of the vagina or nearby lymph nodes, often causing increased bleeding and more severe pain.
Stage 4: The final stage involves metastasis to other organs such as the bladder, intestines, liver, or bones, leading to intense pain and systemic health issues.
Preventing Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer prevention is crucial, as advanced stages are more difficult to treat. Follow these guidelines to reduce your risk:
Practice safe sex: Prevent HPV transmission by using condoms, avoiding multiple sexual partners, and screening for HPV with your partner.
Get vaccinated against HPV: The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing infection. It is recommended for individuals aged 9–45, ideally before the onset of sexual activity.
Undergo regular cervical cancer screenings: Routine Pap smear tests can detect early abnormalities. Women should aim to screen every 1–2 years, especially if they have a history of abnormalities or are at high risk.
Reduce Your Worries – Take Action Today
Stay proactive in safeguarding your health and reduce your worries and prevent the progression of cervical cancer at the Women’s Health Center, Samitivej Chonburi Hospital. We provide comprehensive care for women of all ages, offering cervical cancer screening packages, expert consultation on treatment, and HPV vaccination services.
Appointments can be made at the Women's Health Center, Building A, 2nd Floor, Samitivej Chonburi Hospital, between 08:00-18:00. Call 033-038924.