5 Common Childhood Diseases That Parents Need to Be Prepared
(Pediatrics Center) article author : Admin

5 Common Childhood Diseases That Parents Need to Be Prepared For
Children are more prone to illness due to their weaker immune systems and lack of caution, making them frequent visitors to hospitals. Common childhood illnesses often spread in schools and daycare centers, so parents should be ready to prevent and handle these frequent illnesses in children:
1. The Common Cold
A common cold is an upper respiratory tract infection caused by a virus, one of the most common diseases in children. It can occur year-round, especially when children are exposed to germs or when they have weakened immunity. Symptoms are generally mild, and doctors usually prescribe symptomatic medications like fever reducers, pain relievers and decongestants.
Transmission:
The virus is spread through droplets from coughs and sneezes, breathing in the same air as an infected person, or by touching contaminated surfaces and then rubbing the eyes or mouth. If a child catches a cold, they should stay home from school to prevent spreading the virus. Wearing a mask can also help reduce transmission.
Common symptoms:
- Headache
- Fever
- Nasal congestion
- Difficulty breathing
- Coughing, sneezing, and phlegm
- Sore throat, dry throat
Care guidelines:
Doctors will prescribe medication to treat symptoms, such as fever reducers, painkillers and cough suppressants. Parents can also help lower the fever by giving warm sponge baths, making sure to gently rub the skin to dissipate heat. If the child develops a high fever, immediate medical attention is necessary to prevent seizures.
2. Influenza (Flu)
Influenza is caused by the influenza virus, with two main strains found in Thailand: type A and type B. It is an acute infection that often spreads during cold weather.
Transmission:
The virus spreads through breathing, coughing, or sneezing, often in crowded places, including schools where many children gather.
Common symptoms:
- Headache
- Nasal congestion, runny nose
- Sudden high fever
- Muscle aches
- Loss of appetite
- Dry cough, sore throat
- Nausea and vomiting
- In some cases, diarrhoea
Care guidelines:
It is recommended that children be vaccinated annually against the flu to boost immunity and reduce the severity of the illness. If a child has the flu, doctors will prescribe symptomatic medications and antiviral drugs, which must be taken until the prescribed course is completed. If the child has a fever, it is advisable to give them a sponge bath with warm water to help reduce their temperature.
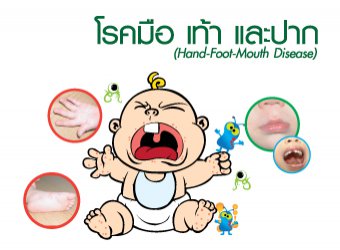
3. Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common illness in young children under 5 and which is caused by Enteroviruses. While not usually severe, it causes discomfort and pain in children, so close monitoring from parents is necessary to prevent complications.
Transmission:
The virus spreads through the digestive and respiratory systems, either by direct contact or through contaminated objects such as toys, food and water. Extra caution is needed, especially during the rainy season.
Common symptoms:
- Blisters that break into sores in the mouth, on the tongue, and in the throat. Some children may also have rashes on their hands, feet, buttocks, and genital area.
- Some cases involve high fever, which parents should monitor closely to prevent seizures.
- Loss of appetite due to mouth sores.
Care guidelines:
There is currently no specific cure for this disease; treatment is primarily symptomatic. Doctors usually prescribe fever reducers, pain relievers or numbing agents for the mouth sores. Symptoms typically last 2-3 days and subside within a week. Parents and guardians may need to provide soft foods for their children. If severe symptoms or complications arise, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
4. Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is caused by the dengue virus which is carried and transmitted by mosquitoes. This disease is common in children during the rainy season due to stagnant water, which increases the chance of mosquito bites. Parents should prevent this by eliminating mosquito larvae and using mosquito repellent spray when children are going outside.
Currently, there is a vaccine to prevent dengue fever, which can be given from the age of 4 (two doses, three months apart). If you live in a high-risk area, it is best to get vaccinated.
Transmission
The disease is spread by mosquitoes, which carry the virus from an infected person in the febrile stage and transmit it to others, leading to illness. Symptoms usually appear 3-15 days after infection.
Common symptoms:
- High fever above 38°C that doesn’t respond well to fever reducers
- Loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting
- Red rash on the body, bleeding gums and blood in the stools or urine
- Severe abdominal pain
If a child experiences a persistent high fever lasting several days, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly, as this may lead to shock.
Treatment
There is currently no specific antiviral drug for dengue fever, so treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as by using fever reducers and giving warm sponge baths. Only take medication prescribed by a doctor, as some fever reducers may increase the risk of bleeding.
Do not use aspirin or NSAIDs to reduce fever. If you are unsure whether the symptoms are from dengue fever, it is best to avoid these medications.
5. Diarrhoea
Diarrhoea is another common illness in children, as they often forget to wash their hands or put things in their mouths, which may lead to viral or bacterial infections and cause diarrhoea. Parents should teach children about hygiene and be cautious of their surroundings to reduce the chance of diarrhoea.
Transmission
It usually occurs when germs enter the mouth through contaminated food or by eating food that has been left out for too long or overnight.
Common symptoms:
- Loose stools more than twice a day, or stools with mucus or blood
- Nausea and vomiting
- High fever
If the child has multiple episodes of diarrhoea and symptoms do not improve, consult a doctor promptly, as dehydration and electrolyte imbalance can lead to shock.
Treatment
If the symptoms are not severe, it’s recommended to give the child oral rehydration solutions or continue with their regular milk. For older children, they should eat soft, freshly cooked food. In severe cases, consult a doctor immediately. The doctor will prescribe medications based on the symptoms and may administer IV fluids depending on the diagnosis.
If a child falls ill, do not ignore it. Monitor their symptoms closely and, if they do not improve or symptoms worsen, see a doctor immediately. Samitivej Chonburi Hospital's paediatric clinic is available 24 hours a day to provide expert care for children with specialised doctors and fully equipped facilities for the most effective and safe treatment.
Make an appointment at the Children’s Health Centre, Building A, 2nd Floor, Samitivej Chonburi Hospital, phone number: 033-038955.